The Internet of Things (IoT) is capable of altering society as we know it. We’re talking about everything — not just computational devices — being locked permanently into a network, churning out and absorbing information ceaselessly.
Is the Future of IoT a Rosy Picture?
Presently, the IoT can be experienced via a multitude of devices filling up homes, offices, factories, and public facilities. The list of connected devices continues to grow by the day, featuring consumer electronics, door locks, vehicle accessories, robotic factory equipment, and more.
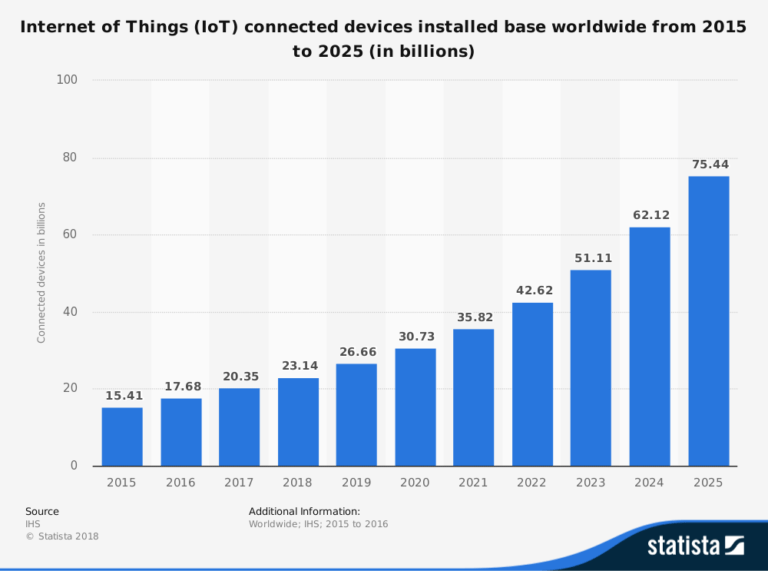
Research shows the number of IoT devices in use across the world amounted to 15 billion in 2015. Experts predict that number will double to over 30 billion by 2020, and explode to 75 billion by 2025. As such, we can expect the IoT to bring about dramatic changes to our everyday lives in the near future.
Imagine an IoT set up in which several components exchange data between themselves in order to carry out pre-configured action sequences without any human intervention. For instance, during a health emergency, your vehicle’s navigation system can show the closest route to a hospital, and at the same time inform the hospital ahead of time to prepare for your emergency.
Despite such IoT wonders, some experts are decrying the complex problems that will result from an IoT future
What is the Internet of Things?
In order to get a good grasp of the IoT future that awaits us, it’s imperative to have a clear understanding of what the IoT is. Basically, an IoT set up comprises various devices that are connected to the internet, generating and sharing data between themselves.
Any item — a building, a seat, animals, and even the human body — can be embedded with chips and sensors which detect and process various types of information, and then integrated into an IoT system. As such, an IoT system can comprise a vast variety of devices, and users can monitor and control these devices from a central interface like a smartphone screen.

In addition, the introduction of 5G is expected to serve as a catalyst for the development of IoT systems. With low latency and high speeds, 5G will supercharge the effectiveness of IoT systems, allowing for quicker exchanges of information between larger collections of devices. This will bring about an unprecedented wave of innovations.
The future of the IoT:
The good
- The rise of AI: Many IoT devices will be imbued with Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is a highly complex algorithm that easily deduces patterns to generate predictions and suggestions. AI-powered devices can also learn to read patterns much better with more use, offering more accurate predictions and recommendations that make life easier for us.
- Smarter routers: Routers serve as the first line of defense for connected devices in an IoT system. They provide a number of security features such as firewalls and passwords to protect vulnerable devices within an IoT system. In the near future, the need for more security in IoT devices will fuel advancements in routers.
- Smarter cars: These days, cars come with various levels of automation, with chips and sensors in various components generating and exchanging actionable information between the parts. In the future, we can expect cars to come with more reliable autonomous capabilities.
- The rise of smart cities: With various organizations such as governments and corporations looking to harness IoT capabilities, we’ll be seeing a rise in the number of IoT systems deployed across cities, giving rise to smart cities
The bad
- DDoS attacks on IoT devices: In 2016, the world witnessed the emergence of the first malware specialized in the IoT. The Mirai malware hacked connected devices such as security cameras, equipment control units and more, accessing these devices through default passwords and names. Further, the malware turned these devices into a botnet used to carry out DDoS attacks on renown websites. This strain of malware is known as open source, meaning it can be modified and reused by any threat actor in the future.
- Vulnerabilities of cloud storage: IoT systems send constant streams of data to the cloud as various components exchange information via the cloud. Massive amounts of data will be stored on the cloud in the IoT era. As a result, data breaches in data centers will have much graver consequences.
- 5G security concerns: Experts predict that, for better convenience, people would prefer to connect to 5G networks directly rather than through a Wi-fi router, and this would expose more devices in an IoT system to cyber attacks. Further, experts believe that 5G is being rushed into the markets with the technology still being premature. They argue that it’s easier to integrate security features into network infrastructures before they’re launched, rather than doing so retroactively to deal with a fault or an attack. But be that as it may, it’s impossible to anticipate all the possible security challenges that might attend 5G without first rolling it out for public use.
The ugly
- DDoS attacks on IoT systems will become even more dangerous: With more devices connected to the internet, cyber criminals will find more entry points to attack IoT systems with. And in a future where a whole lot more devices will be plugged into the cloud, cyber attacks will become more impactful than ever.
- A siege on privacy: As policymakers scramble to enact laws to safeguard against widespread hack attacks, we might witness the enactment of laws that erode our control over our data and online privacy.
Conclusion
The IoT involves virtually every device that communicates with other devices via an internet connection. As basic as such a definition sounds, it’s implications are far-reaching. The IoT is responsible for smart homes and smart cities, as well as smaller consumer devices such as trackers and smartwatches. In fact, virtually any object or thing can be brought into the IoT world.
However, this also means increased security risks and data vulnerability. In general, the IoT has been cited by experts to be cause for concern in certain aspects, mostly dealing with system attacks and data vulnerability. With most technologies and concepts though, soft spots and loopholes tend to exist. The IoT is no different, but it perhaps offers a lot more good and benefits than drawbacks. Thus, the future of the IoT should be looked at with excitement, but security should always be prioritized.
